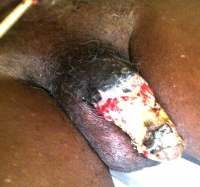
Penile gangrene following penile bandaging for uncontrollable bleeding benign prostatic hyperplasia: case report and review of literature.
Main Article Content
Abstract
Case report: Here, we present the case of a 62-year-old man who had his penis bandaged and suspended for two years following an episode of uncontrollable haematuria following a two-day penile bandage for uncontrollable bleeding BPH in the accident and emergency unit of a tertiary health facility. He subsequently developed penile gangrene necessitating his presentation to our facility after discharging against medical advice. He eventually had suprapubic cystostomy and control of haematuria. Subsequently, he had prostatectomy and penile skin grafting.
Conclusion: This case report emphasizes the challenges of managing bleeding BPH and the d angers of employing unconventional and unorthodox treatment protocol in the management of bleeding BPH.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Journal is owned, published and copyrighted by the Nigerian Medical Association, River state Branch. The copyright of papers published are vested in the journal and the publisher. In line with our open access policy and the Creative Commons Attribution License policy authors are allowed to share their work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. While the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate on the date of its going to press, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher can accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions that may be made. The publisher makes no warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
TNHJ also supports open access archiving of articles published in the journal after three months of publication. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g, in institutional repositories or on their website) within the stated period, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access). All requests for permission for open access archiving outside this period should be sent to the editor via email to editor@tnhjph.com.
How to Cite
References
Fourcade R, Lacoin F, Slama A et al. UP-1.09: Impact of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) on medically treated patients' quality of life. Urology. 2010;76(3):S55.
Maliakal J, Mousa E, Menon V. Giant Prostatic Hyperplasia: Fourth largest prostate reported in medicalliterature. Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal. 2014;14(2):253-256.
Kim J, Moon V. Factors Influencing Health-related Quality of Life in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2010;40(2):287.
Mcvary KT. Clinical evaluation of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Rev Urol2003;5:S3-S11
Mitchell ME, Waltman AC, Athanasoulis CA, Kerr WS Jr, Dretler SP. Control of massive prostatic bleeding with angiographic techniques. J Urol 1976;115:692-5.
Dhingra N, Bhagwat D. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: An overview of existing treatment. Indian J Pharmacol 2011;43:6-12.
Ahmed GI, Aliyu S, Ali N. Bleeding prostate: A 10-year experience in the University of Maiduguri Teaching Hospital (Umth), Nigeria. Sahel Med J 2014;17:79-82.
Yonon H, Goya M, MiyazatoM, Sugaya K, Hatano T, Ogawa Y. Giant prostatic hypertrophy: A case report. Hinyokikakiyo 1990;36:1167-72.
A. Thorpe, D. Neal. Benign prostatic hyperplasia Lancet 2003; 361(9366):1359-1367.Rastinehad AR, Caplin DM, Ost MC, VanderBrink BA, Lobko I, Badlani GH et al. Selective arterial prostatic embolization (SAPE) for refractory haematuria of prostatic origin. Urology 2008;71:181-4.
Mitsubayashi S, Kurita T, Kataoka K, Iguchi M, Kadowaki T. The management of bleeding following transurethral prostatic resection by local irrigation with a thrombin solution. Hinyokikakiyo 1986;32:1371-7.
Singh V., Sinha R. J., Sankhwar S. N. Penile gangrene: a devastating and lethal entity. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation. 2011;22(2):359–361