Epidemiology, Clinical Profile and Management Outcome of Fourniers Gangrene in a Tertiary Teaching Hospital
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Fournier’s gangrene is a polymicrobial necrotizing fasciitis, affecting the genital, perineal and peri anal region which requires prompt and aggressive treatment. This study assessed the prevalence, clinical presentations and management outcome.
Methods: This retrospective observational study involved 39 patients with Fournier’s gangrene managed between January 2020 and December 2024. Socio-demographics, clinical features and management outcome were collated from medical records. Data was analyzed using SPSS version 27.0.
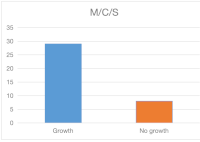
Result: Majority of patients in this study 35.9% of patients are >60 years. The mean age was 51.26+14.37 years. Prevalence of Fournier’s gangrene is 32.27/100,000. Scrotal pain and discoloration were the commonest symptoms in 38 (97.4%) patients. Gangrene involved the scrotum in 39(100%) patients,38 patients (97.4%) had perineal involvement while 24 (61.5%) had penile involvement. Alcohol consumption was the commonest predisposing factor in 19 (48.7%) participants. Amongst etiological factors, anorectal abscess occurred in 15 (44.1%), urethral stricture and epididymoorchitis occurring in 9 (26.5%) patients respectively. E. coli was commonest isolate in 19(65.5%) patients. Thirty-seven (94.9%) patients had urinary diversion while 31 (79.5%) patients had colostomy. Ceftriaxone-based antibiotic and metronidazole were the most used antibiotic combination in 37(94.9%) patients. Patients had a median of 3 debridement with hydrogen peroxide/honey dressing in 36 (92.3%). Majority of patients, 12 (35.3%) had secondary wound closure. Mean duration of admission was 39 days.
Conclusion: The prevalence of Fournier’s gangrene was 32.27/100000. Anorectal abscess being commonest cause. Aggressive wound care with hypertonic saline and honey and a multidisciplinary approach to closure of extensive wound is recommended.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The Journal is owned, published and copyrighted by the Nigerian Medical Association, River state Branch. The copyright of papers published are vested in the journal and the publisher. In line with our open access policy and the Creative Commons Attribution License policy authors are allowed to share their work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. While the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate on the date of its going to press, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher can accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions that may be made. The publisher makes no warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
TNHJ also supports open access archiving of articles published in the journal after three months of publication. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g, in institutional repositories or on their website) within the stated period, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access). All requests for permission for open access archiving outside this period should be sent to the editor via email to editor@tnhjph.com.
How to Cite
References
1.Smith GL, Bunker CB, Dineen MD. Fournier’s gangrene. Br J Urol1998; 81:347-355
2.Pernetti R, Palmieri F, Sagrini E, Negri M, Morisi C, Carbone A, et al. Fournier’s gangrene: Clinical case and review of the literature. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2016; 88(3):237-238
3.Khalid A, Devakumar S, Huespe I, Kashyap R, Chisti I. A Comprehensive Literature Review of Fournier’s Gangrene in Females. Cureus. 2023;15(5):e38953
4.Short B. Fournier gangrene: an historical reappraisal. Intern Med J. 2018; 48(9):1157-1160. doi:10.1111/imj.14031
5.Grzybowski A, Short A. History of Fournier gangrene. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145(2):182 doi:10.1001/arcdermatol.2008.595
6.Fillipone LM. MD Diagnosis: Fournier’s gangrene. Emerg. Med News 2005;27(5):36 oi:10.1097/00132981-200505000-00029
7.Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality,1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200-211. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
8.Radcliffe RS, Khan MA. Mortality associated with Fournier’s gangrene remains unchanged over 25 years. BJU Int. 2020;125(4):610-616. doi:10.1111/bju.14998
9.Bjurlin MA, O’Grady T, Kim DY. Et al. Causative pathogens, antibiotic sensitivity, resistance patterns, and severity in a contemporary series of Fournier’s gangrene. Urology. 2013;81(4):752-758
10.Villanueva-Saenz E, Martinez Hernadez-Magro P, Valdes Ovalle M, Montes Vega J, Alvarez-Tostado FJF. Experience in management of Fournier’s gangrene. Tech Coloproctol. 2002; 6:5-13
11.Paty R, Smith AD. Gangrene and Fournier’s gangrene. Urol Clin North Am 1992; 19:149-162
12.Morpurgo E, Galandiuk S. Fournier’s gangrene. Surg Clin N Am 2002; 82:1213-1224
13. Singh A, Ahmed K, Aydin A, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Fournier’s gangrene. A clinical review. Arch Ital Urol Androl 2016;88: 157-164
14.Mallikarjuna M, Vijayakumar A, Patil V, Shivswamy B. Fournier’s gangrene. Current practices. ISRN Sur 2012;942437
15.Jeong HJ, Park SC, Seo IY, Rim JS. Prognostic factors in Fournier’s gangrene. Int Urol. 2005;12(12):1041-1044
16.Ugwumba FO, Nnambugwu II, Ozoemena OFN. Fournier’s gangrene-analysis of management and outcome in south-eastern Nigeria. S Afr J Surg. 2012; 50(1):16-19
17.Benjelloun EB, Souiki T, Yakla N, Ousadden A, Mazaz K, Louchi A, et al. Fournier’s gangrene: our experience with 50 patients and analysis of factors affecting mortality. World J Emerg Surg. 2013; 8:13
18.Ibadin MO, Akpede GO. A Revised Scoring Scheme for the Classification of Socioeconomic Status in Nigeria. Niger J Paediatr 2021;48(1):26-33
19.Sorensen MD, Krieger JN. Fournier’s gangrene: Epidemiology and outcomes in the general US population. Urol Int. 2016;97(3):249-259
20.Tosun Y, Akinci O, Kucuk HF. Risk factors for mortality in Fournier’s gangrene of anorectal origin. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2022; 28:1128-1133
21.Gul MO, Sunamak O,Kina U, Gunay E, Akyuz. Fournier’s gangrene: Our five -year series and the role of vacuum-assisted closure in the treatment. Niger J Clin Pract 2021; 24:1277-1282
22.Obiesie EA, Nwofor AME, Oranusi CK, Mbaeri TU, Mbonu OO. Prognostic Factors and Outcome of Treatment in Patients with Fournier’s Gangrene in a Tertiary Institution in Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Urology 2020;10(1,2): 12-16
23.Eke N. Fournier’s Gangrene: A review of 1726 cases. British Journal of Surgery. 2000; 87:718-728
24.Salihu M, Liman H, Yusuf S, Umar A, Tunde O, Oshagbemi A. Fournier’s Gangrene: 13-year experience in a Tertiary Center, Northeastern Nigeria. Open Journal of Urology. 2024; 14:407-414
25.Lesso MR, Mwashambwa MY, Msokwa EK. Prevalence, pattern and Early Treatment Outcomes Predictors of Patients with Fournier’s Gangrene at University of Dodoma Affiliated Teaching Hospitals. Int Arch Urol Complic 2024; 10:090
26.Taken K, Oncu MR, Ergun M, Eryilmaz R, Demir CY, Demir M, et al. Fournier’s gangrene: Causes, presentation and survival of sixty-five patients. Pak J Med Sci. 2016;32(3):746-750
27.Chalya PL, Igenge JZ, Mabula JB, Simbila S. Fournier’s gangrene at a tertiary health facility in northwestern Tanzania: a single centre experiences with 84 patients. BMC Res Notes 2015 Sep 28;8: 481.doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1493-1.PMID:26416258; PMCID:PMC4584465
28.Yanar H, Taviloglu K, Ertekin C, Guloglu R, Zorba U, Cabioglu N, et al. Fournier’s Gangrene: Risk factors and Strategies for Management. World Journal of Surgery. 2006; 30: 1750-1754
29.Ozturk E, Ozguc H, and Yilmazlar T. The Use of Vacuum Assisted Closure Therapy in Management of Fournier’s Gangrene. The American Journal of Surgery. 2009; 197:660-665
30.Ayumba BR, Magoha GA. Epidemiological aspects of Fournier’s gangrene at Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi. East Afr Med J. 1998; 75:586-589
31.Joury A, Mahendra A, Alshehri M, Downing A. Extensive necrotizing fasciitis from Fournier’s gangrene. Urol Case Rep. 2019; 26:100943
32.Clayton MD, Fowler JE Jr, Sharifi R, Pearl PK. Causes, presentation and survival of fifty-seven patients with necrotizing fasciitis of the male genitalia. Surg Gynecol Obstet.1990.170(1):49-55
33.You Q, Guan J, Wu B, Du J, Miao Y, Bai X, et al. Fournier’s Gangrene: Clinical case review and analysis of risk factors for mortality. BMC Surgery 2024; 24:251
34. Thwaini A, Khan A, Malik A, Cherian J, Barua J, Shergill I, et al. Fournier’s gangrene and its emergency management. Postgrad Med J. 2006; 82:516-519
35.Citgez S, Demirdag C, Ozkaya M, Selcuk B, Erozenci A. Fournier’s Gangrene: Analysis of Risk Factors Affecting Mortality in a Tertiary Urology Referral Center. J Urol Surg 2019;6(3):196-200
36.Oyelowo N, Ahmed M, Lawal AT, Sudi A, Adetola Tolani AM, Fidelis L, et al. Fournier’s gangrene: Presntation and predictors of mortality in Zaria, Nigeria. Ann Afr Med 2021; 20: 105-110
37.Atila A, Temocin F, Kuruoglu T, Kamali-Polat A. Fournier’s gangrene: An analysis of real- life data. Infect. Dis Clin Microbiol 2023; 1:13-22
38.Aji SA, Alhassan SU, Ujudud MM. Fournier’s Gangrene: Experience with Management of 46 Cases in a Tertiary Institution. Open Journal of Urology 2012; 2:109-112
39.Subrahmanyam M, Ugane SP. Honey dressing beneficial in treatment of Fournier’s gangrene. Indian Journal of Surgery 2004;66(2):75-77
40.Nnabugwu II, Onumaegbu OO, Okolie LT. Fournier’s gangrene: a retrospective review of management outcomes and seasonal variations of clinical presentation. Afr J Urol 2021; 27:66
41.Aliyu S, Ibrahim AG, Ali N, Waziri AM. Fournier’s Gangrene as seen in University of Maiduguri Teaching Hospital. ISRN Urol 2013; 6:17-20