The Variability in the Clinical Presentation of Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Series
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Acute pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a thrombus dislodges from a peripheral part of the body to block any of the branches of the pulmonary artery. Depending on the size of the embolus and the underlying disease state, its presentation can range from being asymptomatic to presenting with sudden death. Its variable nature of presentation frequently leads to a missed diagnosis and increased morbidity or mortality from PE. This series aims to highlight some of the variable presentations of acute pulmonary embolism with the objective of stimulating a high index of suspicion, which can lead to early diagnosis and treatment.
Method: The electronic medical records of 3 patients in a private hospital in Abuja were selected for the series, together with a review of the existing literature. Consent to use patient information was obtained from the patients, and the approval for the case series obtained from the head of the department of research of the hospital.
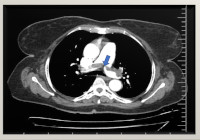
Result: The clinical presentation of acute PE was highly variable in all 3 cases, with the least symptomatic case having a saddle-embolus lodged at the bifurcation of the pulmonary artery. Electrocardiographic tracings were also different in all 3 cases.
Conclusion: The prognosis of PE depends on early diagnosis and treatment. Mortality and morbidity from this condition can be reduced with a background knowledge of its variable clinical presentation and a high-index of suspicion.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Journal is owned, published and copyrighted by the Nigerian Medical Association, River state Branch. The copyright of papers published are vested in the journal and the publisher. In line with our open access policy and the Creative Commons Attribution License policy authors are allowed to share their work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. While the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate on the date of its going to press, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher can accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions that may be made. The publisher makes no warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
TNHJ also supports open access archiving of articles published in the journal after three months of publication. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g, in institutional repositories or on their website) within the stated period, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access). All requests for permission for open access archiving outside this period should be sent to the editor via email to editor@tnhjph.com.
How to Cite
References
Uchechukwu C, Wilson K, Lowe R et al. Pulmonary Embolism. Physiopedia.2.Piazza G, Goldhaber S. Acute Pulmonary Embolism Part 1: Epidemiology and Diagnosis. Circulation. 2006;114: e28–e32.
Ouellette D, Harrington A, Kamangar N. Medscape: Pulmonary embolism: Epidemiology. 2020 Sept.
Andersson T, Soderberg S. Incidence of acute pulmonary embolism, related comorbidities and survival; analysis of a Swedish national cohort. BMC Cardiovasc Discord 17, 155 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-017-0587-1.
Gupta R, Ammari Z, Dasa O, et al. Long-term mortality after massive, submassive, and low-risk pulmonary embolism. Vascular Medicine. 2020;25(2): 141-149. Doi: 10.1177/1358863X19886374.
Morrone D, Morrone V. Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Focus on the Clinical Picture. Korean Circ J. 2018 May;48(5):365-381. Doi: 10.470/kcj.2017.0314.
West J, Goodacre S, Sampson F. The value of clinical features in the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism: Systematic review and meta-analysis, QJM. International Journal of Medicine. 2007;100(12): 763-769. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcm113
Carson JL, Kelley MA, Duff A et al. The clinical course of pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 07;326(19): 1240-5.
Girard P, Decousus M, Laporte S et al. Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism in patients withproximal deep vein thrombosis: specificity symptoms and perfusion defects at baseline and during anticoagulant therapy. AM J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 164:1033-7.
Sadeghi A, Brevetti GR, Kim S et al. Acute massive pulmonary embolism: role of the cardiacsurgeon. Tex Heart Inst J. 2005;32(3):430-3. PMID: 16397945; PMCID: PMC1336727.
Vyas V, Goyal A. Acute pulmonary embolism. [Updated 2022 May 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560551/
Huisman M, Klok F. How I diagnose acute pulmonary embolism: Blood. 2013;121(22): 4443-4448. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-03-453050
Patel P, Patel P, Bhatt M et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of test accuracy for the diagnosis of suspected pulmonary embolism. Blood advances. 2020 Sep 22;4(18):4296-311.
Tapson VF. Acute pulmonary embolism.N Engl J Med. 2008 Mar 6. 358(10): 1037-52. [Medline].
Boka K, Soo Hoo G. Pulmonary Embolism Clinical Scoring Systems. Medscape. 2020 Dec.
Roy P, Douillet D, Penaloza A. Contemporary management of acute pulmonary embolism. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2022;32(5): 259-268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2021.06.002.
Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur Heart J. 2020;41(4): 543-603.
Levis JT. ECG Diagnosis: Pulmonary Embolism. Perm J. 2011;15(4): 75. PMID: 22319421.
Rashid M, Al Mogbil M, Shah I, Moin S, Aquil N. Classic S13T3 in Lobar Pneumonia, otherwise popularly associated with Pulmonary Embolism. International J of Advances in Case Reports. 2015;2(11):684-685.
Shopp D, Stewart L, Emmett T, Kline J. Findings From 12-lead Electrocardiography That Predict Circulatory Shock from Pulmonary Embolism: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2015 Oct;22(10):1127-37.
Konstantinies S, TorbickiA, Agnelli G et al. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2015;68: 6410.1016/j.rec.2014.12.002.