Biopsy-Confirmed Lupus Nephritis with Advanced Sclerosing Disease Managed with Overlap Treatment. A Case Report
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Lupus nephritis, complicating systemic lupus erythematosus, can progress to end-stage kidney disease, with a poor prognosis. Histological diagnosis is essential in formulating an effective treatment regimen particularly with symptom overlap.
Method: We highlighted the role of a histological diagnosis in the management of Lupus nephritis with complex overlapping symptoms according to approved treatment protocol.
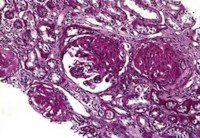
Result: She was anemic and the histological diagnosis was class VI lupus nephritis. She was managed using an overlapping treatment spanning classes IV – VI, with haemodialysis (HD), mycophenolate mofetil, methylprednisolone and diuretics based on heightened disease activity and extrarenal manifestations. Using the WHO and the International Society of Nephrology/Renal Pathology Society revised guidelines, KDIGO recommended haemodialysis for classes III, IV, and V with nephrotic syndrome, in addition to high dose corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide/MMF (induction therapy), and low dose corticosteroid/MMF for maintenance therapy. The disease went into remission, and she continued outpatient HD.
Conclusion: The case highlights the place of histological diagnosis in managing LN associated with complexities of staging and symptoms-overlap to achieve optimal results.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The Journal is owned, published and copyrighted by the Nigerian Medical Association, River state Branch. The copyright of papers published are vested in the journal and the publisher. In line with our open access policy and the Creative Commons Attribution License policy authors are allowed to share their work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. While the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate on the date of its going to press, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher can accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions that may be made. The publisher makes no warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
TNHJ also supports open access archiving of articles published in the journal after three months of publication. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g, in institutional repositories or on their website) within the stated period, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access). All requests for permission for open access archiving outside this period should be sent to the editor via email to editor@tnhjph.com.
How to Cite
References
Pons-Estel GJ, Ugarte-Gil MF, Alarcón GS. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017; 13(8):799-814. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2017.1327352.
Fatoye F, Gebrye T, Mbada C. Global and regional prevalence and incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus in low-and-middle income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2022; 42(12):2097-2107. doi: 10.1007/s00296-022-05183-4.
Green MR, Kennell AS, Larche MJ, Seifert MH, Isenberg DA, Salaman MR. Natural killer T cells in families of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Their possible role in regulation of IgG production. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: 303–310.
Devadass CW, Mysorekar VV, Eshwarappa M, Mekala L, Siddaiah MG, Channabasappa KG. Clinical features and histological patterns of lupus nephritis in a single center of South India. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016; 27(6):1224-1230. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.194657.
Adelowo OO, Oguntona SA. Pattern of systemic lupus erythematosus among Nigerians. Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 28(6):699-703.
Parikh SV, Nagaraja HN, Hebert L. et al. Renal flare as a predictor of incident and progressive CKD in patients with lupus nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2014; 9: 279–284
Bajema IM, Wilhelmus S, Alpers CE, Bruijn JA, Colvin RB, Cook HT, et al. Revision of the International Society of Nephrology/Renal Pathology Society classification for lupus nephritis: clarification of definitions, and modified National Institutes of Health activity and chronicity indices. Kidney Int. 2018; 93(4):789-796. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.11.023.
Uduagbamen PK, Salako BL, Hamzat MA, Kadiri S, Arogundade FA. Kidney Function in Frequent Users of Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Open J Int Med 2020; 10(1): 69-82. doi: 10.4236/ojim.2020.101007
KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int suppl. 2012 2(2):139-274
Malvar A, Pirruccio P, Alberton V, Lococo B, Recalde C, Fazini B, et al. Histologic versus clinical remission in proliferative lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017; 32(8):1338-1344. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv296.
Rovin BH, Parikh SV, Alvarado A. The kidney biopsy in lupus nephritis: is it still relevant? In: Ginzler EM, Dooley MA (eds). Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2014, pp. 537–552