Radiologic Spectrum of Foreign Body Introduction into the Body among Paediatric Patients seen at the Rivers State University Teaching Hospital, Port Harcourt
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60787/tnhj.v22i4.614Keywords:
Foreign body, foreign body inhalation, foreign body in children, Port Harcourt, foreign body ingestionAbstract
Background: Foreign body ingestion in children is a common domestic accident and so vigilance cannot always prevent the introduction of foreign body into one of their natural orifices. Foreign body can be any object originating from outside and intruding through any of the body’s orifices. The aim of this research is to evaluate the radiologic spectrum of foreign body introduction into the body amongst paediatric patients.
Method: This is a cross-sectional descriptive study design was adopted for the study from patients referred for radiologic investigation for suspected foreign body in the body from July 2020 to December 2020. The variables were collated, documented, and analysed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) windows version 23.0 statistical software (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL) and presented in tables, charts and graphs.
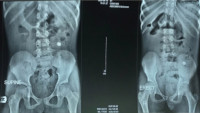
Results: Females constituted 47.46% (n=28) while males were 52.54% (n=31) with a female to male ratio of 1:1.127. Age range of participants was 10 months to 72 months, with a mean age of 38.66 + 15.84 months. Oral route was the most frequent route of introduction of foreign bodies into the body accounting for 74.58% (n = 44), with earrings (22.03%) been the most common materials followed by wedding rings 18.64% (n=11). Batteries, coins, rings, and keys were also ingested or inhaled.
Conclusion: Appropriate radiologic investigation is essential as radiology remains a veritable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of foreign body introduction into body through the body orifices.
Downloads
References
Litovitz TL, Klein-Schwartz W, WhiteS, CobaughDJ, YounissJ, OmslaerJC, et al. 2000 annual report of the American association of Poison control centres, toxic exposure surveillance system. Am J Emerg Med 2001; 19: 337-395.
Oburra HO, Ngumi ZW, Mugwe P, Masinde PW, Maina AW, Irungu C. Bronchoscopy for removal of aspirated tracheobronchial foreign bodies at Kenyatta National Hospital, in Kenya. East Cent AfrJ Surg.2013; 18:48-57.
Gulshan H, Mahid I, Sharafat AK, Muhamad I, Javed Z. An experience of 42 cases of bronchoscopy at Saidu group of teaching hospitals, SWAT. J Ayub Med Coll Abottabad. 2006; 18:59-62.
Onotai LO, Ibekwe MU, George IO. Impacted foreign bodies in the larynx of Nigerian children. J Med Med Sci. 2012;3:217-21.
Narasimhan KL, Chowdhary SK, Suri S, Mahajan JK, Samujh R, Rao KL. Foreign body airway obstruction in children. J IndianAssoc Pediatr Surg. 2002;7:184-9.
Onotai LO, Ebong ME. The pattern of foreign body impactions in the tracheobronchial tree in University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital. Port Harcourt Med J. 2011; 5: 130-5.
Adegboye VO, Adebo OA. Epidermiology of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in Ibadan. Niger J Clin Pract. 2001; 4: 51-3.
Gilyoma J, Chalya P. Endoscopic procedures for the removal of foreign bodies of the aerodigestive tract: The Bugando Medical Centre experience. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2011;11:1-5.
Evans JNG. Foreign bodies in larynx and trachea. In: Kerr, editor. Scott-Brown’s Otolaryngology. London: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1997.
Rovin JD, Rodger MB. Pediatric foreign body aspiration. Pediatric Review 2000;21:86-90.
Tan HKK, Brown K, McGill T, et al. Airway foreign bodies (FB): a 10year review. Int/Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol 2000; 56: 91-9.
Murty PSN, Vijendra S Ingle, Ramakrishna S. Foreign body in the upper aerodigestive tract. SQU Journal forScientific Research Medical Sciences 2001;3(2):117-20.
Khan NU, Nabi IU, Yousaf S. Foreign bodies in larynx and tracheobronchial tree. Pak Armed Forces Med J 2000;50(2):68-70.
Schmidt H, Manegold BC, Foreign body aspiration in children. Surg Endosc 2000;14(7):644-8.15.Monte CU. Foreign Body Ingestion in Children American Family Physician. 2005; 72(2):287-291.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal and Publisher

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Journal is owned, published and copyrighted by the Nigerian Medical Association, River state Branch. The copyright of papers published are vested in the journal and the publisher. In line with our open access policy and the Creative Commons Attribution License policy authors are allowed to share their work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. While the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate on the date of its going to press, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher can accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions that may be made. The publisher makes no warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
TNHJ also supports open access archiving of articles published in the journal after three months of publication. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g, in institutional repositories or on their website) within the stated period, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access). All requests for permission for open access archiving outside this period should be sent to the editor via email to editor@tnhjph.com.